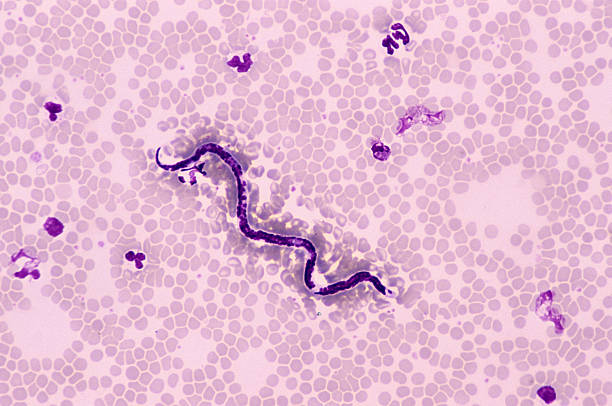
If you want to prevent the disease cause by parasites in your body, you need to know how to treat them.
Getting rid of immune complexes
Most people aren’t aware that the human immune system has hundreds of subtypes. Each one is designe to fight off the other, and they’re good at it. But the best of the best are ephemeral and can only survive for a few days. Getting rid of these microbes is no easy feat, but it is doable. The key is to figure out which ones to kill first. To do this, you’ll need to understand the microbiome and how it interacts with other cells. Luckily, you have a few innately competent friends who are willing to help. They know a thing or two about parasites, and know when to give you the benefit of the doubt. イベルメクチン 通販 medication is fight to parasites infection.
While the human body is host to dozens of species, the most common are bacteria and fungi. These critters are not exactly symbiotic and can be a thorn in your side. But, with the right strategies, you can keep them at bay. This includes a well-designe immune response system, and the proper use of antibiotics. Of course, all this is assuming you’re not living in an isolate cave, and have a healthy diet and exercise regimen. So, if you are in the market for a new home, do the research and you’ll be reward in the form of a healthier and more vibrant you.
Altering the DC activities
The human body is home to a myriad of microorganisms. Some are benign and some are downright parasitic. Despite their presence, some of these infect cells can survive despite the best efforts of their hosts. They elude detection by antibiotics or the host’s digestive enzymes. They can also escape the wrath of the immune system through a process known as quiescence.
During this state of affairs, the synthesis of viral proteins is significantly reduced. Consequently, a number of factors are release into the bloodstream, most of which can be characterize as a phenotype. One of the best known is the CHIPS protein of S. aureus. Interestingly, this protein binds to the C5a receptor of the host’s neutrophils. This interaction has been dubbed the ‘human’s miracle’ by scientists who have been examining the effect.
Several viruses, like the aforementioned, inhibit or prevent DC function. Others, like the Coxiella burnetii, stultify maturation. It’s also possible to be a quiescent bacterium with no cell dividing capacity. Although this is a relatively rare occurrence, it’s not unheard of. In fact, some strains of T. gondii have been shown to inhibit migration of the human DCs. For instance, a low virulent strain of the aforementioned has been find to inhibit the migratory abilities of human DCs in vitro. As a result, this little critter possesses the ability to thrive in environments where it completes its life cycle.
Interfering with phagocytic activity
Parasites have several strategies to evade the host immune response. These strategies can be classifie into three categories: inhibition, camouflage, and suppression. This review outlines the current knowledge about parasites’ immune evasion mechanisms. Understanding their mechanisms is important to design diagnostics and vaccines.
Infection with parasites often causes amoebic infections. These are characterize by an interplay between pathogenic factors and the host’s immune system. Some parasites produce human blood group antigens. Moreover, many parasites share antigen sequences with the host’s self-antigens. However, they can also use host factors to hide from the host’s immune system.
For example, Leishmania donovani promastigotes inhibit phagosome maturation. Furthermore, they suppress synaptotagmin V recruitment. They also inhibit phagosome acidification. Finally, they produce a polyanionic proteolytic proteoglycan that is functionally similar to cobra venom factor. Using this molecule, they block the alternative complement pathway and activate the classical complement pathway.
The parasites’ ability to evade the host immune response is important for protract parasitism. During infection, they antagonize the immune system regulatory network. As a result, they suppress the production of protective antibodies. Thus, they survive.
Despite their efforts, they do not completely destroy the infect cell. Their presence on the surface of the cell inhibits the clonal expansion of T cells. It is therefore difficult for the T cell to recognize the infect cell. Instead, the T cell becomes paralyzed.
Several species of arthropods, especially the nematodes, are invertebrate pharmacologists. These animals consume a large number of fleas. Because of this, they are likely expose to permanent microbiological challenges. Consequently, the cost of their defenses is high.
Invading organ systems
Parasites are single cells or multicellular organisms that infect and damage host organisms. There are a variety of parasites including protozoa, viruses and helminths. Each type has different effects and a host’s immune system must defend itself against these microorganisms.
Although there are many species of parasites, there are three major classes of parasites that cause disease in humans. These are the helminths, protozoa, and endoparasites.
Helminths, also known as worms, invade the human gut and skin. This parasite infection can be very mild, causing diarrhea and mild itching, or it can be severe, causing flu-like symptoms and dehydration. Some helminths, such as trichomoniasis, can cause no symptoms, but can produce an unusual discharge in the genital area.
Protozoa are small, single-cell organisms that live outside the body and are find in insect bites and contaminate food. They can infect the bloodstream, lungs, heart, and liver. In some cases, they can even affect the immune system.
The liver is a special organ that enables the parasites to multiply and hide from the immune system. It is also an important site of attrition, a process in which a parasite loses its ability to survive.
The liver is also a place where a parasite’s eggs can become a cyst, a fluid-fill structure that can disrupt organ function. Cysts can also disrupt the normal function of the heart and lungs.
Ectoparasites
Ectoparasites are a wide variety of parasitic organisms that can invade your body. These parasites are often responsible for spreading diseases. Some ectoparasites can be quite invasive, producing large, painful skin lesions. Luckily, most of these organisms cannot survive without their hosts.
Ectoparasites include fleas, lice, ticks, mites and other arthropods. They can be find on humans and companion animals. If you notice an infestation, it is best to get it treated.
When you visit a doctor, he or she can perform a series of tests to diagnose the infestation. He or she might order blood and serology tests, magnetic resonance imaging scans, or computerize axial tomography scans. The results of these tests will help identify the exact type of parasite you are infect with.
When you are diagnose with a parasite infection, your doctor may prescribe Ziverdo kit medication to treat the condition. Treatment depends on the type of parasite and the symptoms you are experiencing. For example, if you are experiencing an allergic reaction to a certain insect, your doctor may prescribe an anti-histamine or a steroid to combat the itch.
Other common parasites are protozoa, which are single-cell organisms that live outside of the body. Protozoa can spread through contaminate food or person-to-person contact. This can lead to conditions such as pneumonia or food poisoning.
To avoid getting sick with a parasitic infection, you need to eat properly cook meat and drink water from seal bottles. You should also consult a veterinarian to develop a treatment plan for your parasite infestation.